Fundamental Rights in India are the basic human rights guaranteed by the Indian Constitution. These rights protect citizens from discrimination, injustice, and abuse of power. Every Indian citizen should understand Fundamental Rights in India to live with dignity, freedom, and equality. These constitutional rights form the foundation of democracy and justice in the country.
Let us clearly understand all six Fundamental Rights in India

1. Fundamental Rights in India – Right to Equality
The Right to Equality is one of the most important Fundamental Rights in India. It ensures that every person is treated equally before the law without discrimination based on caste, religion, gender, or place of birth.
This right provides:
- Equal protection of laws
- Equal opportunity in public employment
- Abolition of untouchability
- Removal of social inequality
The Right to Equality strengthens justice and fairness in Indian society.
2. Fundamental Rights in India – Right to Freedom
The Right to Freedom provides essential personal liberties to citizens. Among this right protects individual liberty and democratic values.
It includes:
- Freedom of speech and expression
- Freedom to assemble peacefully
- Freedom to move and reside anywhere in India
- Freedom to practice any profession
The Right to Freedom empowers citizens to express their opinions without fear.
3.Right Against Exploitation
The Right Against Exploitation is a vital part of Fundamental Rights in India. It protects people from forced labor, child labor, and human trafficking.
This right ensures:
- Protection against forced work
- Ban on child labor in hazardous industries
- Prevention of human trafficking
It safeguards human rights in India and protects vulnerable communities.
4. Fundamental Rights in India – Right to Freedom of Religion
Freedom of religion is a core value of Fundamental Rights in India. This right allows citizens to practice, profess, and propagate any religion freely.
It also ensures:
- Religious equality
- Secular governance
- Peaceful coexistence of all religions
The Right to Freedom of Religion promotes unity in diversity across India.
5.Cultural and Educational Rights
Cultural and Educational Rights protect the identity of minority communities. These Rights are allow citizens to preserve their language, culture, and traditions.
These rights include:
- Right to conserve culture and language
- Right to establish educational institutions
- Protection of minority education rights
They help maintain India’s cultural diversity and heritage.
6. Fundamental Rights in India – Right to Constitutional Remedies
The Right to Constitutional Remedies is known as the heart of Fundamental Rights in India. It allows citizens to approach the Supreme Court and High Court if their rights are violated.
Courts can issue writ petitions such as:
- Habeas Corpus
- Mandamus
- Certiorari
- Prohibition
- Quo Warranto
This right ensures that constitutional rights are properly enforced.
Conclusion – Importance of Fundamental Rights in India
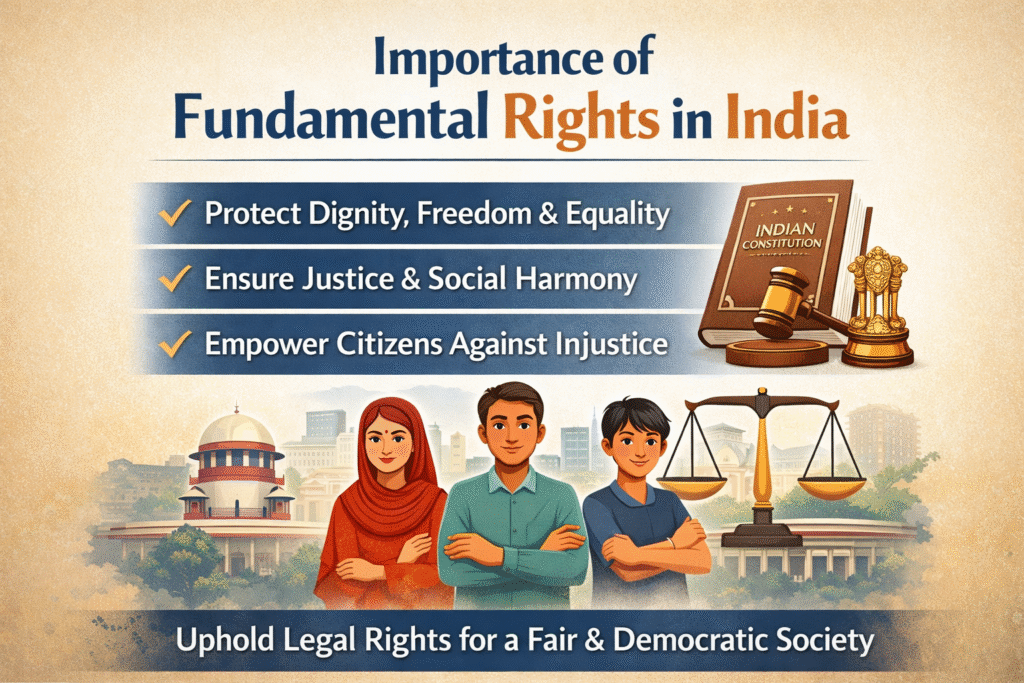
Fundamental Rights in India play a vital role in protecting the dignity, freedom, and equality of every citizen. These constitutional rights ensure justice, social harmony, and democratic values in the country. Awareness of legal rights of citizens helps people take correct legal action against discrimination, injustice, and unlawful activities.
Understanding the rights of Indian citizens empowers individuals to safeguard their personal liberty and social status. If any of your Rights are violated, approaching the Supreme Court and High Court or consulting a legal expert can help you protect your rights effectively.